*A new algorithm planner developed by the Robotics Institute of the University of nekemelon makes the best task allocation between humans and robots *. As robots increasingly join people's work in factories, workshops, warehouses and other places, the complexity and importance of deciding who will do what work are also increasing.
People are more suitable for doing some work, and robots are more suitable for doing some work. In some cases, it is beneficial to spend time teaching robots to do a task and reap rewards later.
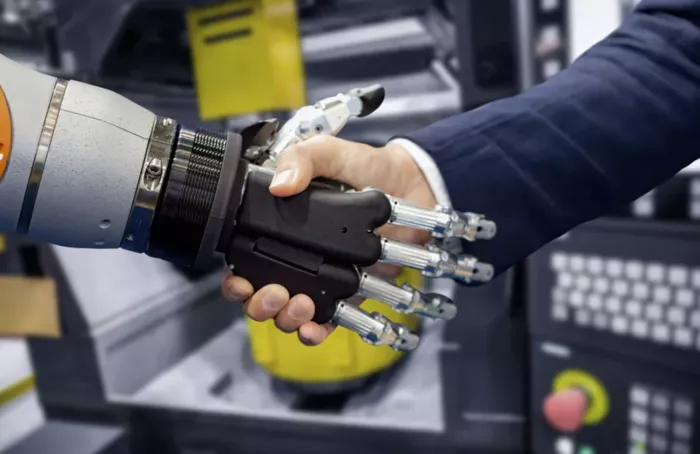

Researchers at the Robotics Institute (RI) at Carnegie Mellon University have developed an algorithm planner to help delegate tasks to humans and robots. The planner, called action, empowerment or learning (ADL), considers a range of responsibilities and determines how best to allocate them. The researchers asked three questions. When should the robot take action to complete the task? When should a task be entrusted to mankind? And when should robots learn a new task?
The team's work can be valuable in manufacturing and assembly plants, sorting parcels, or in any environment where humans and robots work together to accomplish several tasks. To test the planner, the researchers set up some scenes where humans and robots had to insert blocks into nailboards and stack components made of Lego blocks of different shapes and sizes.
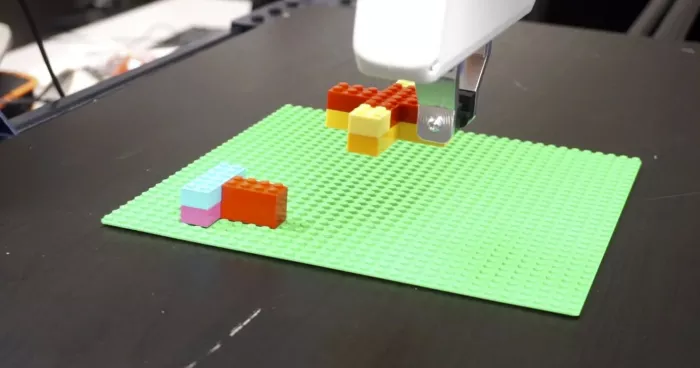
Using algorithms and software to decide how to delegate and divide labor is not new, even if the robot is part of the team. However, this work is one of the first to incorporate robot learning into its reasoning. Usually in manufacturing, a person will manually operate a manipulator to teach a robot how to complete a task. Teaching robots takes time, so the initial cost is very high. But in the long run, it may be beneficial if robots can learn a new skill.
Part of the complexity is deciding when to teach robots, rather than delegating tasks to humans. This requires the robot to predict which tasks it can complete after learning new tasks. Considering this information, the planner transforms the problem into a mixed integer program, which is an optimization program commonly used in scheduling, production planning or designing communication network, which can be effectively solved by ready-made software. The planner performs better than the traditional model in all instances, and the cost of completing the task is reduced by 10% to 15%.