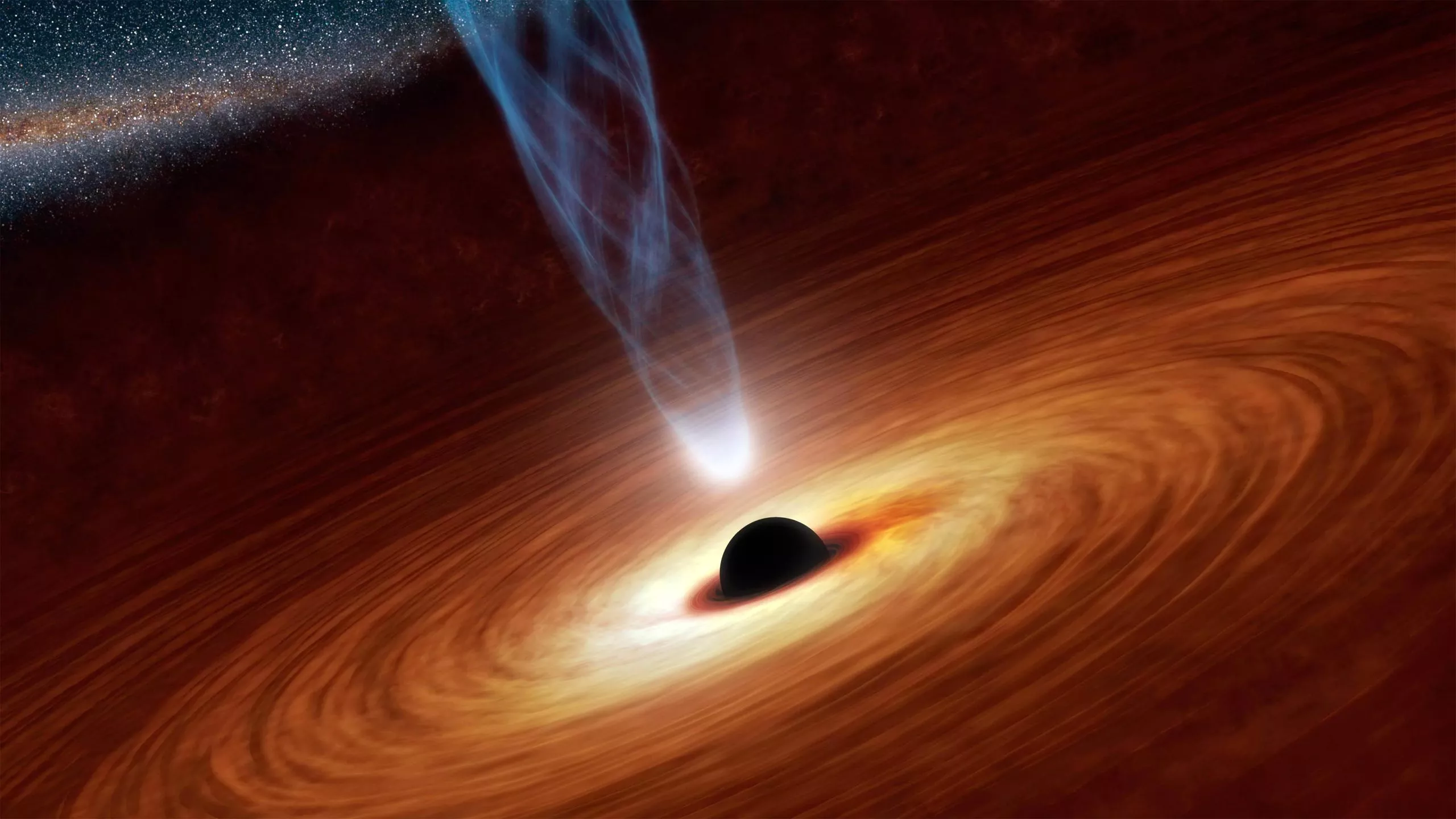
At the end of 2018, the gravitational wave observatory LIGO announced that they had detected the furthest and largest source of space-time ripples in history: gravitational waves caused by the collision of a pair of black holes in deep space. Since 2015, scientists have been able to observe these invisible celestial bodies, which can only be detected by their gravitational attraction. Then, in a breakthrough in 2019, the event horizon telescope (EHT) captured images of black holes and their shadows for the first time.

The history of human search for these mysterious objects can be traced back to the 18th century, but the key stage occurred in an appropriate dark period in human history - World War II.
The natural philosopher John Michel and later Pierre Simon Laplace first considered the concept of an object capable of capturing light so that the rest of the universe could not be seen in the 18th century. Using Newton's law of gravity, they calculated the escape speed of light particles from an object, and predicted the existence of stars so dense that light could not escape from them. Michell calls them "dark stars".
But after the discovery of light in the form of waves in 1801, it was unclear how light would be affected by Newton's gravitational field, so the idea of dark stars was abandoned. About 115 years later, Albert Einstein proposed the general theory of relativity in 1915. A year later, Carl Schwarzschild solved this problem, which enabled scientists to understand how light in the form of waves would behave under the influence of gravitational field.
In addition, Schwarzschild also predicted the existence of the critical circumference of a celestial body - Schwarzschild radius. It is reported that light cannot pass through because it exceeds this circumference. The idea is similar to Michelle's, but now the critical perimeter is understood as an insurmountable obstacle.
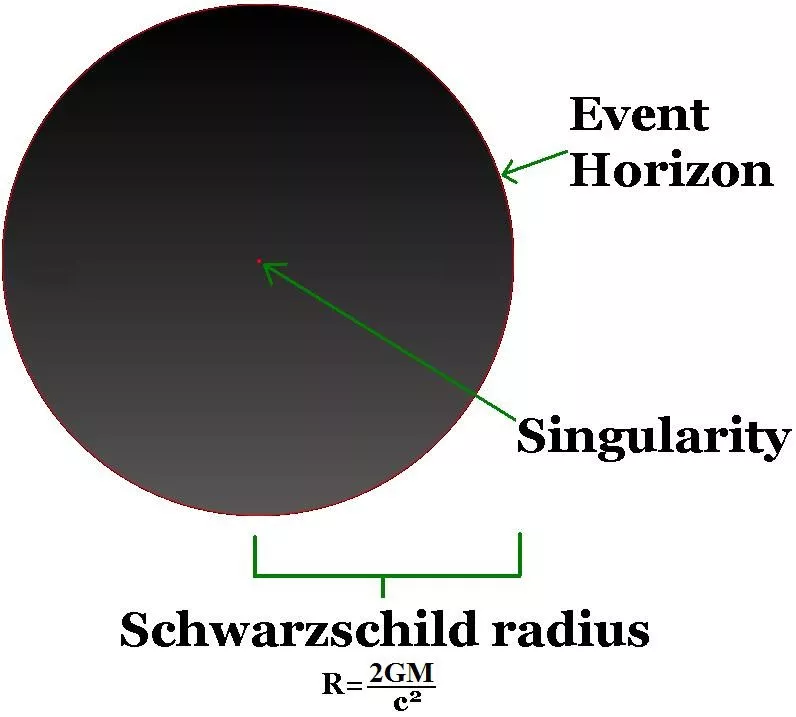
It was not until 1933 that George lemet showed that this impenetrability was just an illusion for distant observers. Using the now famous examples of Alice and Bob, the physicist hypothesized that if Bob stood still and Alice jumped into the black hole, Bob would see Alice's image slow down until it solidified before reaching the Schwarzschild radius. Lemet also pointed out that in reality, Alice crossed the barrier. Bob and Alice just went through different events.
Despite this theory, at that time, no known celestial body had such a size, and nothing even approached a black hole. Therefore, no one believes that something similar to the dark star assumed by Michelle will exist. In fact, no one even dared to take this possibility seriously - until the Second World War.
From dark stars to black holes
On September 1, 1939, the Nazi German army invaded Poland, which led to the beginning of the war that changed world history forever. It is worth noting that on this day, the first academic paper on black holes was published. J-robert Oppenheimer and Hartland Snyder, two American physicists, published their now acclaimed article on the continuous gravitational contraction, which is a key point in the history of black holes. This point in time is particularly strange when considering the central position of the rest of World War II in the development of black hole theory.
This is Oppenheimer's third and last paper on astrophysics. In this paper, he and Snyder predicted that a star would continue to shrink under the influence of its own gravitational field and form a strongly attractive object - even light could not escape from it. This is the first version of the modern concept of black hole. Black hole is a huge celestial body, which can be detected only through its gravity.
In 1939, it was still a strange idea that people couldn't believe. It will take 20 years until the concept is developed enough for physicists to begin to accept the consequences of continuous contraction described by Oppenheimer. The second world war itself played a vital role in its development, because the U.S. government invested in the research of atomic bomb.

Reborn from ashes
Of course, Oppenheimer is not only an important figure in the history of black holes. He later became the head of the Manhattan Project, which led to the development of atomic weapons.
Politicians understand the importance of investing in science to bring military advantage. Therefore, on the whole, it has extensive investment in revolutionary physics research related to war, nuclear physics and the development of new technologies. A wide variety of physicists are committed to such research, and as a direct consequence, most of the fields of cosmology and Astrophysics have been forgotten, including Oppenheimer's papers.
Despite the loss of a decade of large-scale astronomical research, the discipline of physics as a whole flourished in the war - in fact, military physics finally strengthened astronomy. The United States became the center of modern physics in the war. The number of doctors has risen sharply and a new tradition of postdoctoral education has been established.
By the end of the war, the study of the universe was rekindled. The once underestimated theory of general relativity has also revived. The war has changed the way we do physics: in the end, it has brought due recognition to the fields of cosmology and general relativity. This is the basis of accepting and understanding black holes.
Subsequently, Princeton University became the center of a new generation of relativists. It was there that nuclear physicist John Wheeler, who later popularized the name "black hole", first came into contact with general relativity and re analyzed Oppenheimer's work. At first, he was skeptical, but on the day the war broke out, that is, September 1, 1939, the influence of close relativity, the new progress of computational simulation and the development of radio technology made him the most enthusiastic person of Oppenheimer's prediction.
Since then, new properties and types of black holes have been theorized and discovered, but all of these reached a climax in 2015. The measurement of gravitational waves generated in black hole binary system is the first concrete proof of the existence of black hole.