Brushing your mobile phone before going to bed at night may have become a habit of many young people. Some studies have warned that frequent cell phone brushing before going to bed may be harmful to health. For example, a long time of cell phone brushing may affect falling asleep and disturb the normal sleep pattern and biological clock. Others worry that brushing the mobile phone before going to bed will aggravate negative emotions. In fact, neuroscientists have indeed found through animal experiments that increasing light at night, especially blue light irradiation - electronic devices such as mobile phones usually emit blue light, which will affect specific neural circuits of the brain and induce depression related symptoms.
However, a recent research survey conducted by the University of Copenhagen in Denmark on young people brushing their mobile phones late at night found that the impact of brushing their mobile phones before going to bed may not be as serious as we thought, and may also play a positive role.
The researcher's paper published in scientific reports said: "contrary to the popular assumption, the use of smart phones before bedtime is not closely related to poor mental health. This may be because the use of smart phones is also a social behavior, which has associated benefits to mental health."

The data of this study comes from a follow-up survey of more than 800 Danish college students. The researchers provided smart phones to the college students who participated in the survey, obtained their use frequency through the customized software running in them, and collected data for four weeks.
According to the data, during the self-reported sleep of these young people in 16 working days (from Monday night to Thursday night), the software recorded more than 250000 smartphone activities, including answering calls, sending messages, posting or like on social media platforms.
At the beginning of the survey and four months after the follow-up, the researchers also assessed the mental health status of these young people through questionnaires, including loneliness, depressive symptoms, stress level, life satisfaction and so on. Then, statistical analysis was used to eliminate potential confounding factors. The researchers examined whether the participants' mental health status was related to the use of mobile phones during sleep.
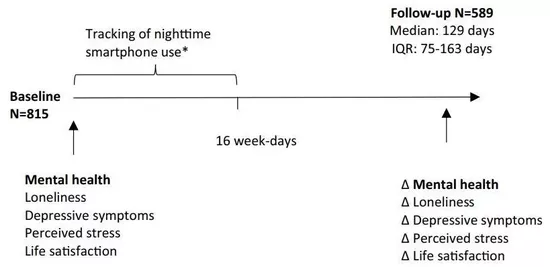
According to the baseline data, compared with the participants who did not brush their mobile phones at night, the participants who slept continuously for less than 6 hours due to using their mobile phones had higher stress perception and depression symptoms at the beginning of the survey. However, during the average follow-up period of four months, there was no clear correlation between sleeping on the mobile phone and changes in perceived stress, loneliness and life satisfaction.
The researchers also noted that, compared with the participants who did not brush their mobile phones at night, the depression symptoms of the participants who brushed their mobile phones at multiple nights (although the proportion was not high) even decreased slightly from baseline to follow-up.
The study speculates that this slight change may be due to the fact that these scenes of using mobile phones are a social phenomenon beneficial to mental health. For the participants in this study - college students, the formation of social networks and participation in social interaction are crucial to their mental health. Therefore, although brushing mobile phones at night may disturb sleep, the beneficial effects of social contact may offset some of the negative consequences.
In the paper, the researchers speculated that according to other previous studies, such as a survey of 300 deep smartphone users in the United States, anxiety is related to the type of mobile phone brushing activities. For example, compared with social interaction, access to news, entertainment, consumption, etc. are more closely related to anxiety. Therefore, the research team plans to further investigate whether the type of mobile phone brushing activities before going to bed also has different effects on mental health.