On May 5, Beijing time, according to foreign media reports, when climbers climb Mount Everest, they usually have to carry oxygen bottles, which is a necessary equipment for them to breathe freely at high altitude. The closer we get to the edge of the earth's atmosphere, the less oxygen we can get. In contrast, the oxygen at sea level is very abundant.
This is just an example of how the earth's atmosphere changes with altitude. From the troposphere near sea level to the outermost exosphere, all levels of the earth's atmosphere have different basic components. According to the national weather service, the beginning and end of each layer of atmosphere are determined by four key characteristics: temperature change, chemical composition, density and internal gas movement.
So, considering these four characteristics, where does the earth's atmosphere end? Where does outer space begin? Each layer of the earth's atmosphere plays its own role, including preventing carcinogenic cosmic radiation and providing the pressure required to form liquid water, thus ensuring that the blue planet can accommodate a variety of life forms.
The farther away from the earth's surface, the smaller the density of the atmosphere, and its composition has changed. Lighter atoms and molecules begin to dominate, while heavier molecules still stay near the earth's surface. When you rise in the atmosphere, the pressure or weight of the atmosphere above you will decrease rapidly. Although commercial aircraft have pressurized compartments, rapid changes in height still affect the slender eustachian tube connecting the ears, nose and throat. This is why our ears may have tinnitus when the plane takes off.
Eventually, the air will become too thin for traditional aircraft to produce enough lift to fly. This is the area designated by scientists, marking the end of the atmosphere and the beginning of outer space. This line is called the K á RM á N line and is named after Theodore von Carmen, a Hungarian American engineer and physicist. Carmen became the first person to try to define the boundary between earth and outer space in 1957.
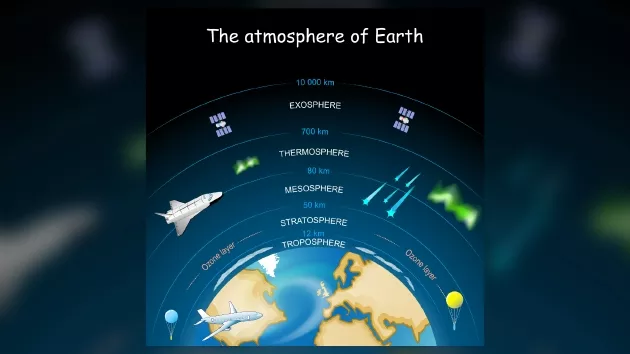
The vertical structure of the earth's atmosphere can be roughly divided into troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere
The Carmen line marks the boundary between the earth and space. It not only indicates the altitude limit of aviation flight, but also is very important for spacecraft and satellites to successfully orbit the earth. The Carmen line is a rough area, which means that above this altitude, the satellite will be able to orbit the earth at least once without burning or out of orbit.
This boundary is usually defined as about 100 kilometers from the earth's surface as the boundary between atmosphere and space (however, this definition is not accepted by all organizations. For example, the US Air Force and NASA define the boundary between atmosphere and space as 80 kilometers, and there is no provision on this boundary in international law at present). It is possible for an object to orbit the earth at a height below the Carmen line, but it requires extremely high orbital speed, which will be difficult to maintain due to the existence of friction. Many people may feel that the Carmen line is an imaginary but actual threshold between air travel and space travel.
For a satellite, many factors such as its size and shape will determine how much air resistance it will encounter, so as to determine its ability to successfully orbit the earth. Due to the resistance of the earth's outermost atmosphere, LEO satellites will gradually slow down and usually leave orbit after several years of operation. According to the European Space Agency, the altitude of low earth orbit satellites is usually below 1000 kilometers, but sometimes as low as 160 kilometers.
However, this does not mean that the earth's atmosphere cannot be detected 1000 kilometers away. In the area where satellites operate, the atmosphere does not disappear. It will take thousands of kilometers before the evidence of the earth's atmosphere will disappear. The outermost atoms of the earth's atmosphere, the hydrogen atoms that make up the corona (the luminous part of the exosphere), can even extend beyond the lunar orbit (in other words, if we take the exosphere as part of the atmosphere rather than part of outer space, the atmosphere can extend to the sky at an altitude of about 10000 kilometers).
So, if we could cross the Carmen line, what would we observe? Will we realize that we are crossing the boundary between earth and space? The answer is no, we won't observe any special changes. Generally speaking, the stratification of the atmosphere is basically based on the physical properties of the atmosphere itself, but the Carmen line is not a physical boundary in essence, but a relatively abrupt boundary defined based on some factors in the aerospace field; Therefore, people will not notice the process of crossing this boundary, and it has no thickness. However, because the gas in the atmosphere scatters the blue visible light more than the visible light of other colors, a blue halo will appear at the edge of the atmosphere; As the altitude rises, the atmosphere becomes thinner and thinner, and the blue halo will gradually disappear, leaving only the black space as the background.
As the flight altitude of the aircraft rises, the air becomes thinner and thinner, and it will provide less and less lift. In order to keep flying in the air, the aircraft needs higher and higher speed. According to this trend, the speed required to ensure that the aircraft can fly in the air will reach the orbital speed of that altitude at a certain altitude. Above this altitude, aerodynamics fails and space begins to work. In fact, the calculation result of the height of Carmen line is not exactly 100 kilometers, but Carmen still suggests that 100 kilometers above sea level should be used as the boundary between outer space and the earth's atmosphere. On the other hand, the atmosphere is also changing from time to time, and various parameters vary from time to place, and the calculation results are not constant. Therefore, although the value is 100 kilometers, the Carmen line is not an absolutely accurate and strict definition. After being adopted by the international aviation Federation, the Carmen line has become a widely accepted boundary in various related fields.
If someone can get to the Dhaka gate line, even for a short period of time, is it possible to survive? What if you're near the Carmen line but don't have a custom spacesuit or an oxygen tank for climbing? Can we breathe at such a high altitude? Can birds reach this height?
Scientists say it is possible in principle for birds to fly all the way to the Carmen line, but in reality, animals cannot survive above the "Armstrong limit". Armstrong's limit is located at an altitude of about 20 kilometers from the ground, where the pressure is very low, causing the fluid in the lungs to boil.
