As we all know, heat sink is the main part of PC cooling technology. Heat spreaders and heatsinks are used for both passive and active cooling, but the research team recently found a solution that looks better, more personalized and more fashionable**
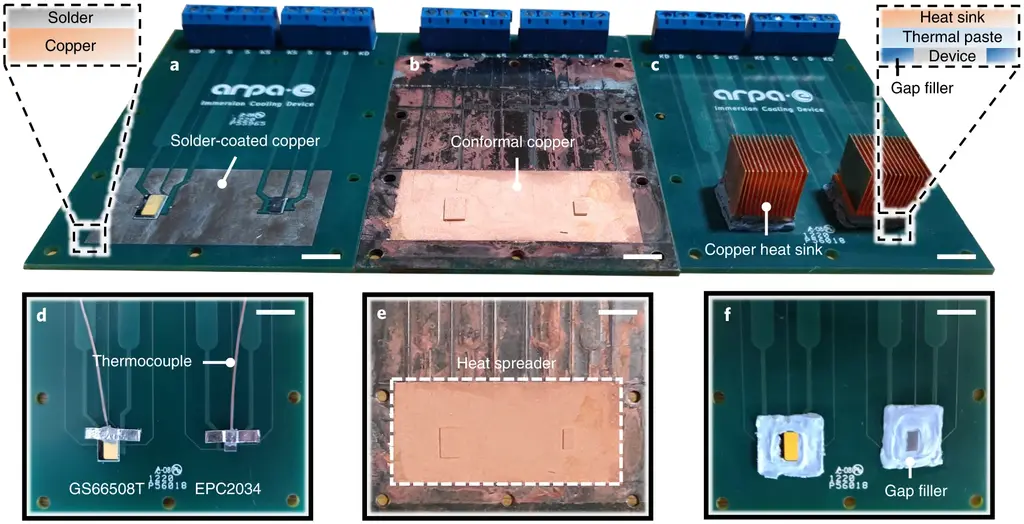
The team, composed of experts from the University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign (UIUC) and the University of California at Berkeley (UC Berkeley), described their experiments and findings in the paper "high efficiency cooling via the monolithic integration of copper on electronic devices".
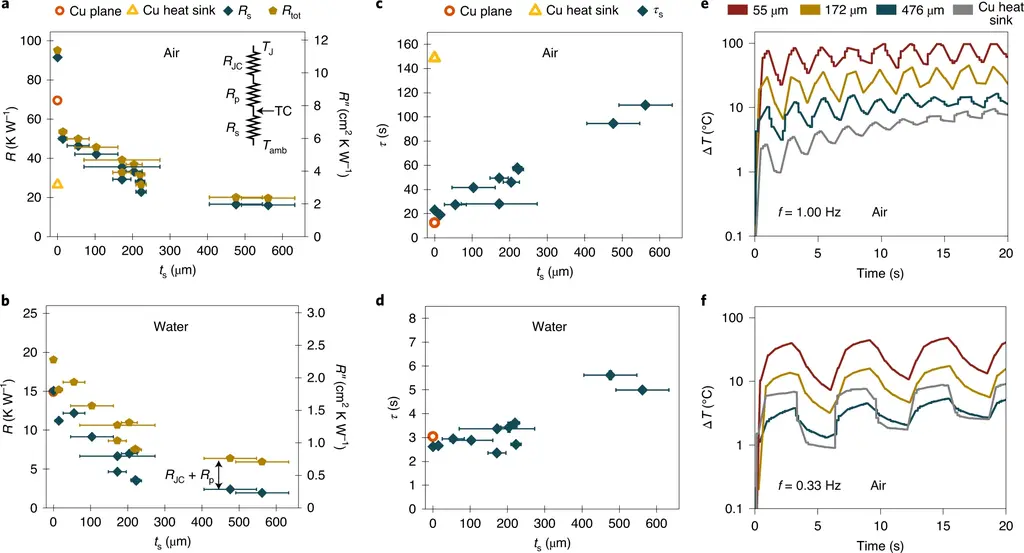
The highlight of the new copper conformal coating technology is that it occupies little physical space in the equipment and is more efficient than the current copper radiator. The researchers demonstrated a 740% increase in power per unit volume.
The lead author of the paper, Dr. Tarek gebrael of UIUC, explained that there are three main problems with traditional radiators. First of all, the unique and efficient conductive materials used in the most advanced heat sink are expensive and difficult to expand the scale. Gebrael clearly illustrates his point by referring to the radiator containing diamonds as a competitive technology.
Second, the traditional design connects soaking fins and heat sinks in series. "In many cases, most of the heat is generated under electronic devices," gebrael lamented. Third, the best soaking sheet cannot be directly installed on electronic equipment, but needs thermal interface materials to inhibit the best performance.
Difference between soaking fin and heat sink
The top of the soaking plate has a large and flat surface. They have no fans and fins. Instead of forced air cooling, the radiator is pressed directly on another large plane and allows heat to be transferred from the small radiator to the larger metal surface. The soaking plates themselves do not cool the CPU, they only transfer heat to another object that can be safely emitted from the processor. Soaking plates are ideal for systems that are expected to operate under extreme shock and vibration, or systems that need to be completely sealed in containers to protect them from the environment.
▲ in the above figure, the right side is the soaking fin and the left side is the heat sink
A heat sink is a traditional cooling solution that maximizes surface area (using fins or fins) and airflow (using fans) to dissipate heat from the processor into the surrounding air. The radiator with built-in cooling fan is a simple, lightweight and completely independent cooling solution. Depending on the airflow available, they can usually outperform radiators of similar sizes.
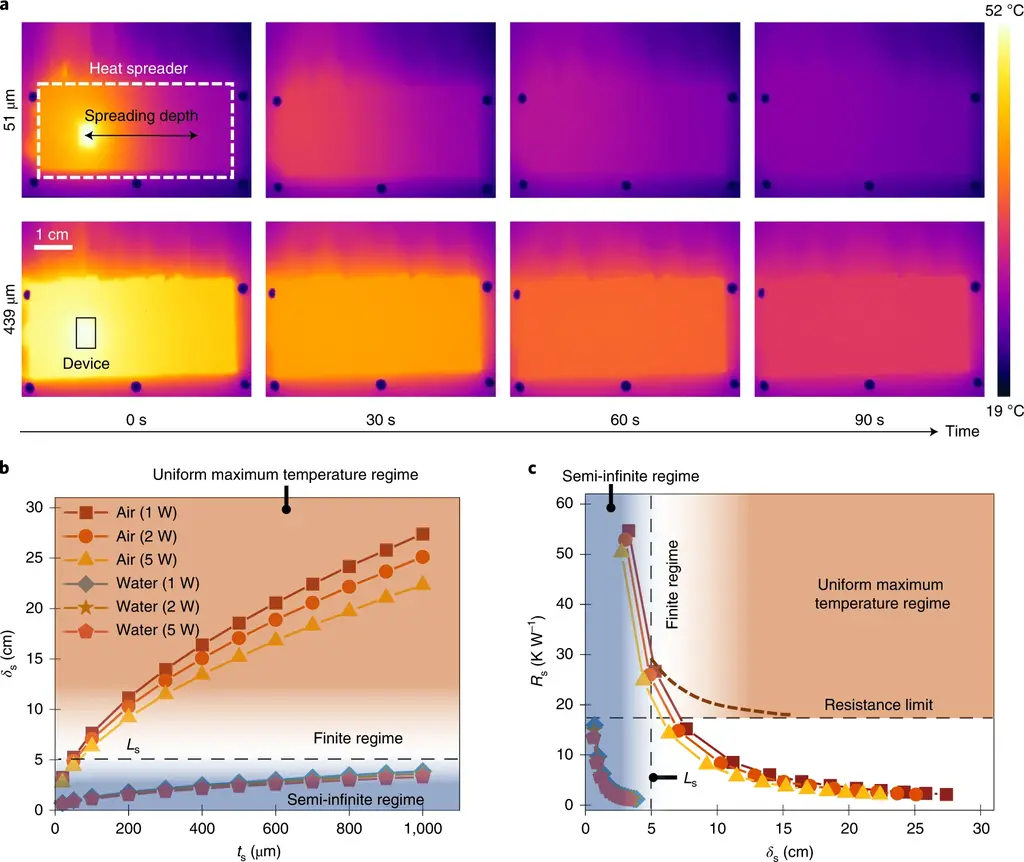
So, how can the new technology solve all the above shortcomings of the current heat dissipation methods? The new radiator coating covers the entire equipment, creating a large cooling surface area.
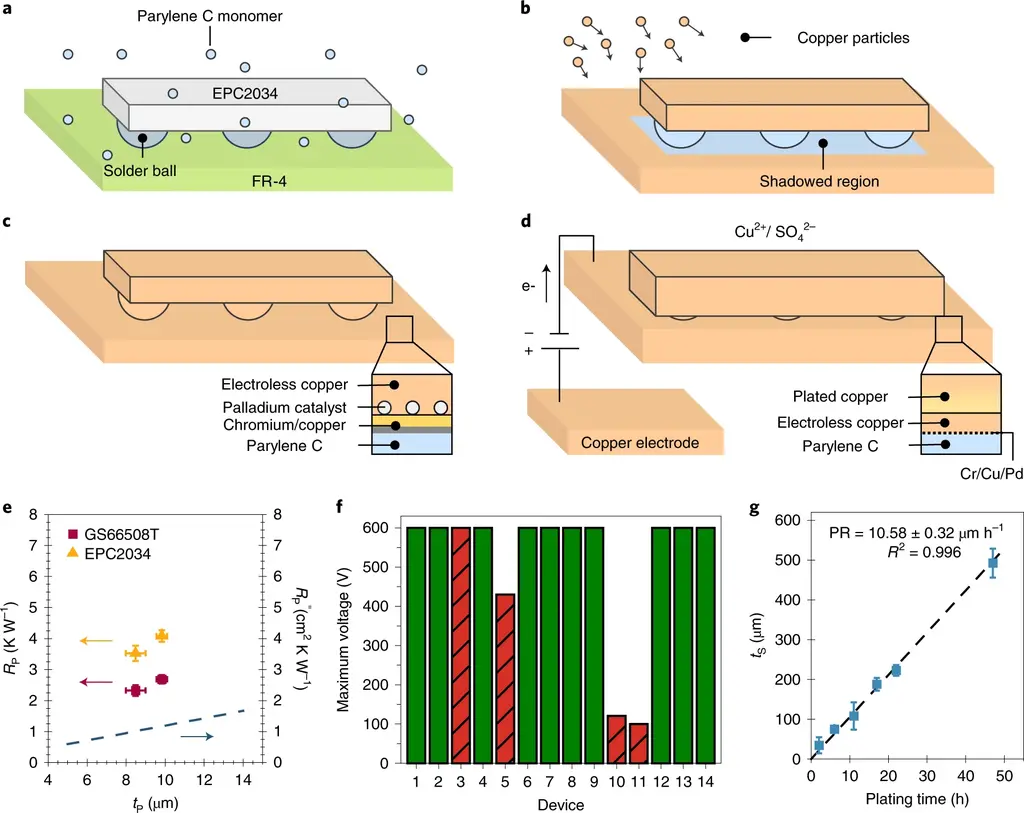
Wrote in the paper:
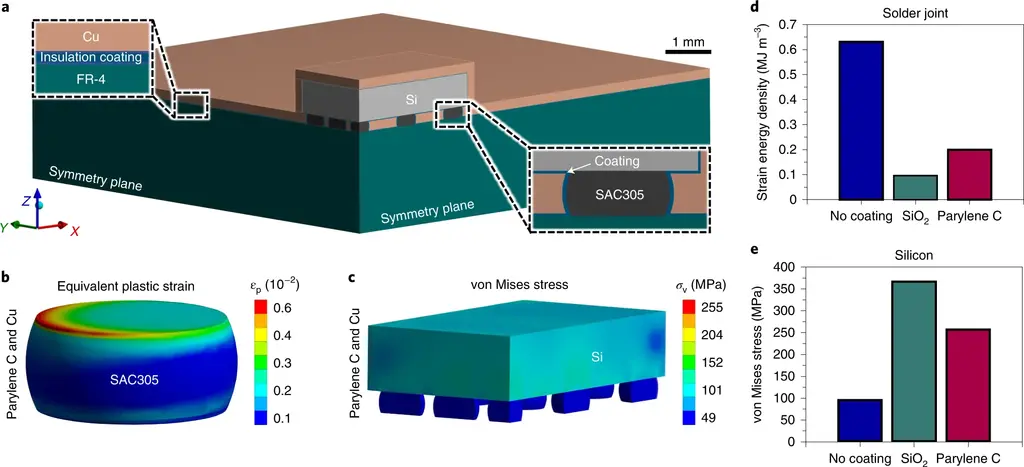
Firstly, a layer of poly (2-chloro-p-xylene) (poly-p-xylene) (poly-p-xylene C) electrical insulation layer is coated on the equipment, and then a layer of copper conformal coating is coated.
Compared with the prior art, this makes copper close to the heating element, eliminates the demand for thermal interface materials and provides better cooling performance.
This coating technology eliminates any large area of copper or aluminum outcrops, so it is a more compact solution that can suck heat away from fast-running processors and memory. According to the researchers, thin conformal coating and no bulky traditional radiator can provide higher unit volume power, up to 740%.
"When you use our coating, you can stack more printed circuit boards in the same volume than traditional liquid or air-cooled radiators," gebrael said. The researchers next plan to verify the durability of the coating, which is an important step in industry acceptance. In addition, the researchers plan to test in immersion cooling and high-pressure environment. In the initial test, the researchers used "simple" PCBs, but they hope to expand the test of cooling technology on hot electronic devices such as "full-size power modules and GPU cards".