One of the biggest weather - affecting features on Mars is dust. Because Mars is smaller than the earth, its gravity is lower, about one third of that of the earth. And Mars also has a thin atmosphere, whose density is only 1% of the earth's atmosphere. Taken together, these two facts mean that the Martian surface is experiencing rapid temperature changes and strong winds. These winds blow up small particles of dust on the surface and form dust storms to roll in various regions, sometimes even across the whole planet.

This means that the dust has a great impact on the Martian environment, in some cases, so serious that winter ends early. Not to mention the impact on Mars explorers. For example, the 15 year mission of the Mars rover Opportunity ended because a dust storm blew dust on its solar panels, making it impossible to charge the rover's batteries.
But it turns out that dust not only shapes the Martian weather -- it also shapes the Martian surface. A recent study published in the Journal of geophysical research: planes found that the strange dust avalanche may be related to a mystery about frost.
The study used data from the ancient Mars Odyssey mission, an orbiter launched in 2001, when it took images of the surface of Mars. There are three scientific instruments on the orbiter, including an instrument for measuring radiation, a spectrometer and an imager. The imager can be observed with visible and infrared wavelengths, which are used to capture surface images. This is the beginning of the problem.
Invisible frost
Images taken by Odyssey's visible light instrument show frost on the slopes of the Martian surface, which appears as blue stripes. The existence of frost makes sense. When the sun set on Mars, it became extremely cold, with surface temperatures as low as minus 200 degrees Fahrenheit. This cold caused a certain amount of carbon dioxide in the Martian atmosphere to freeze into dry ice.
However, when the researchers compared the images with infrared images, they saw more of the ice spread over a larger area. Infrared images can show heat because hot objects release infrared energy. This means that the infrared instrument can also detect cold, because it can see areas with less infrared energy release. In infrared images of the same Martian slope, the researchers saw cold patches scattered outside the frost patches they saw in visible light images.
At first, they thought it might mean frost beneath the surface. Lucas Lange, an intern at NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory who participated in the study, said: "our first idea is that ice may be buried there. But this explanation is not consistent with their understanding of the observed environment. There are a lot of dry ice near the poles of Mars, but we are looking for places closer to the equator of Mars, where it is usually too hot to form dry ice."
Solve the mystery

In this regard, researchers believe that dust must be mixed with ice to form a "dirty ice". They cannot be seen in the visible light band, but they can still be seen in the infrared. Chris Edwards of the University of Northern Arizona, one of the authors of the research paper, said that this is a process on Mars that is different from anything on earth. "Every time we send a mission to Mars, we find new strange processes. We don't have the same thing as the slope stripes on earth. You must understand Mars beyond your experience on earth," he said
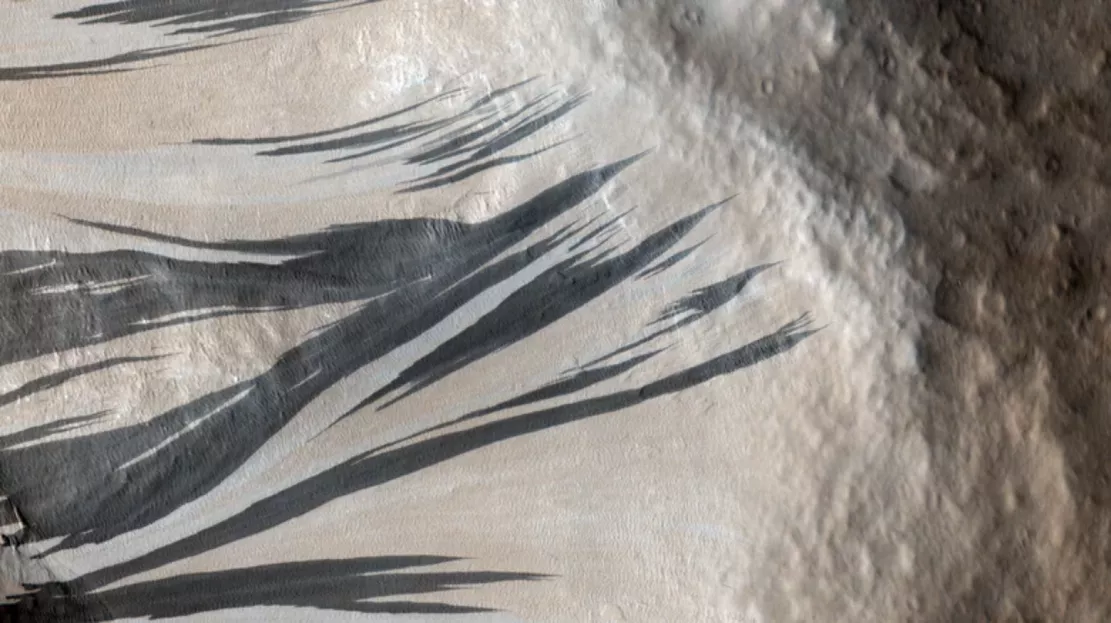
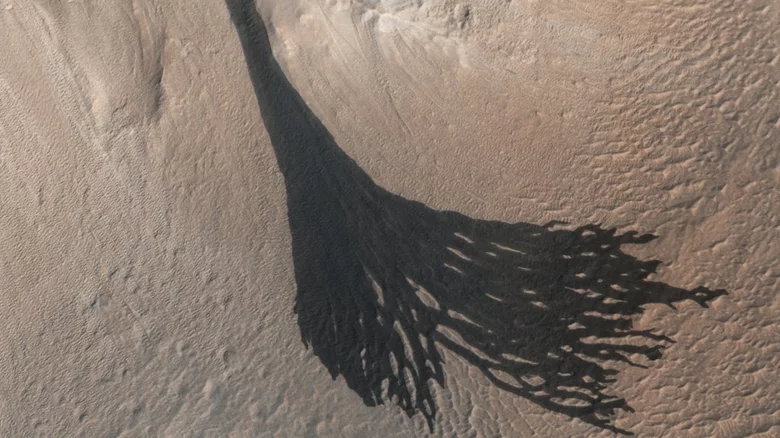
New research finds that when the sun rises on Mars, dry ice melts very quickly because the atmosphere is very thin. The ice sublimes to produce winds, which can sometimes be strong enough to blow the dust on the surface. On a steep slope, this may cause dust avalanches. The presence of this dry ice near the earth's surface helps to produce these dust avalanches, resulting in dramatic dark streaks seen from orbit.
This dirty frost may also explain some dramatic features of the Martian surface. On some slopes of Mars, you can see black lines called slope stripes, which can extend to 3300 feet long. The researchers suspect that the streaks were caused by a dust avalanche - because the dust moved along the slope and exposed the darker rocks below. Therefore, the interaction of dust and frost is reshaping the landscape of Mars in a way we have never seen on our own planet.